
In wet AMD,
all fluid is pathological1-4
-
The presence of fluid damages retinal structure and function1
- Unresolved fluid may lead to greater damage of the photoreceptors, worsening of vision, and ultimately blindness2,3
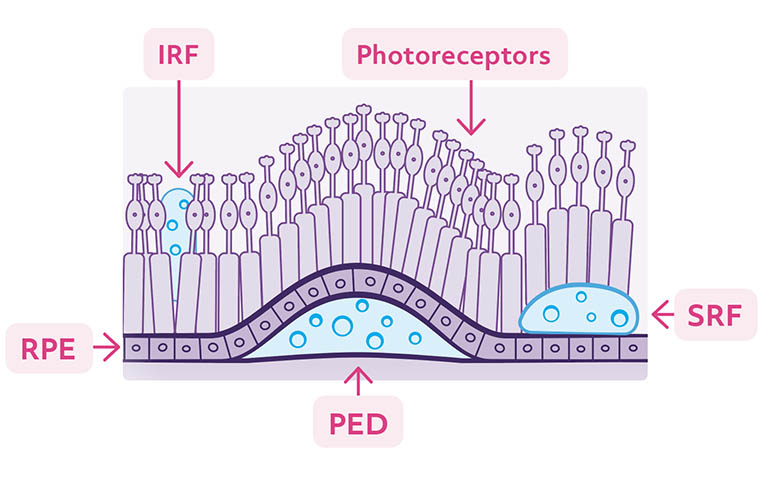
Resolving fluid may be key to achieving vision outcomes4,5*
-
According to a retrospective analysis of HAWK and HARRIER that used deep-learning volumetric analysis to assess the response of retinal fluid to anti-VEGF therapy, a lower level of ANY fluid is associated with better VA outcomes4,5
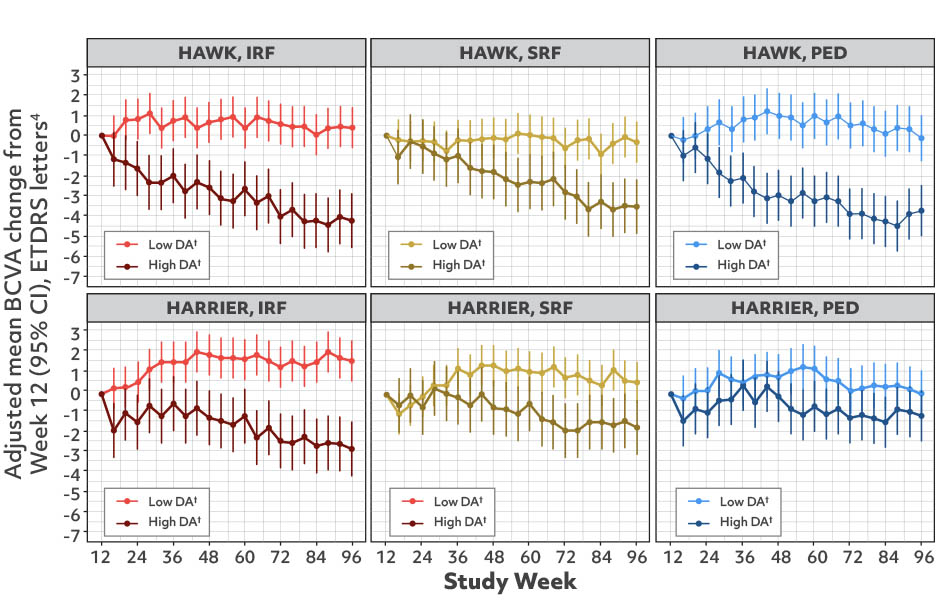
According to a retrospective analysis,6
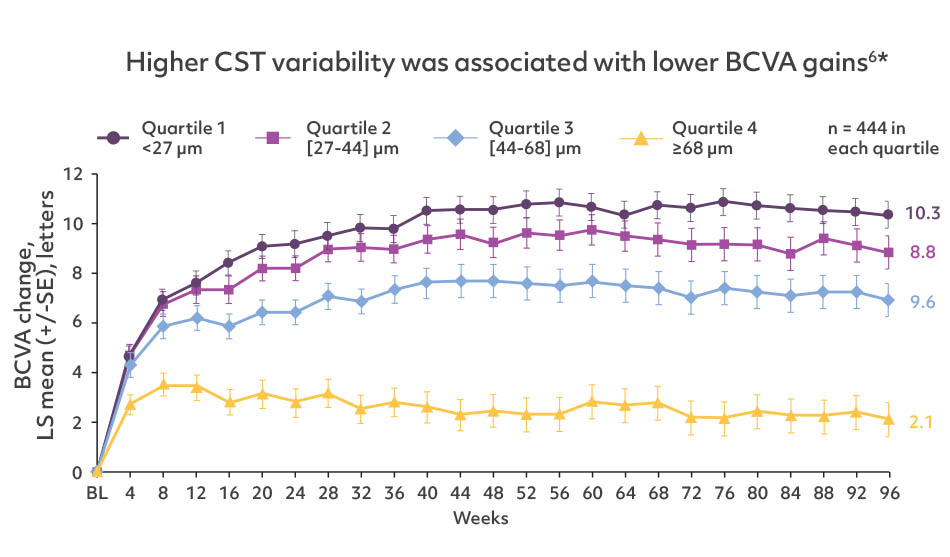
Reducing CST may lead to disease control and better VA outcomes6*
- Greater CST variability throughout treatment was associated with worse visual outcome6
Unmet needs exist for many patients9,10
Unresolved fluid and increased treatment frequency
Retrospective analyses of electronic health records from the USRetina and IRIS databases9,10
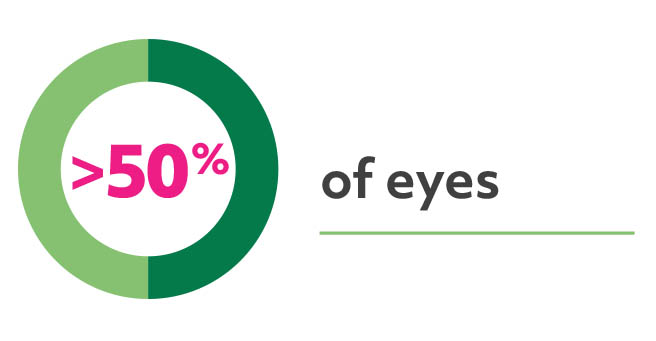
had residual fluid after 2 years in real-world patients receiving treat-and-extend regimens with aflibercept, ranibizumab, or bevacizumab9
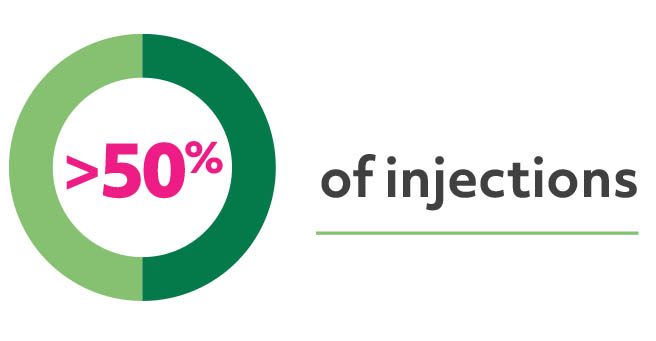
over the course of the first year were given more often than every 8 weeks10
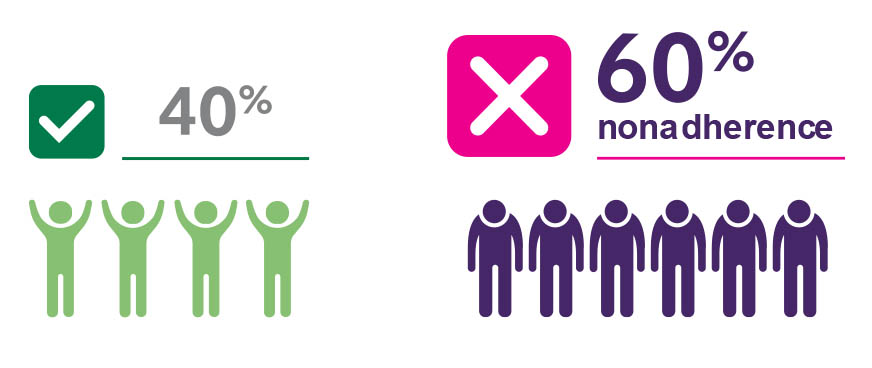
Adherence is a challenge in wet AMD11-14
- Nonadherence is a prevalent problem, with up to 60% nonadherence at 24 months’ follow-up14


Rate this content: