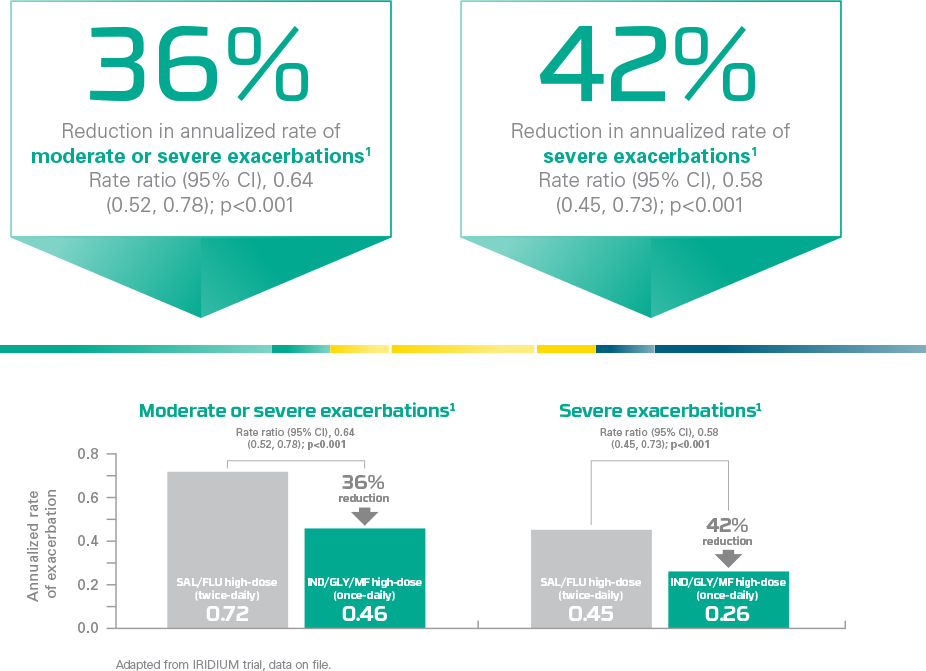
ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® provides substantial reduction of asthma attacks*
In a secondary analysis,** ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® high-dose (once-daily) reduced exacerbations vs. SAL/FLU high-dose (twice-daily)
Primary endpoint was met:
ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® significantly improved trough FEV1 by +76mL (95% CI: 41,111) and +65mL (95% CI: 31, 99) at Week 26 vs. IND/MF for medium - and high-doses respectively, p<0.001.1
Key secondary endpoint, improvement in ACQ-7 score for ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® vs. IND/MF at Week 26, was not met; however all five arms demonstrated similarly high and clinically relevant improvement from baseline.1
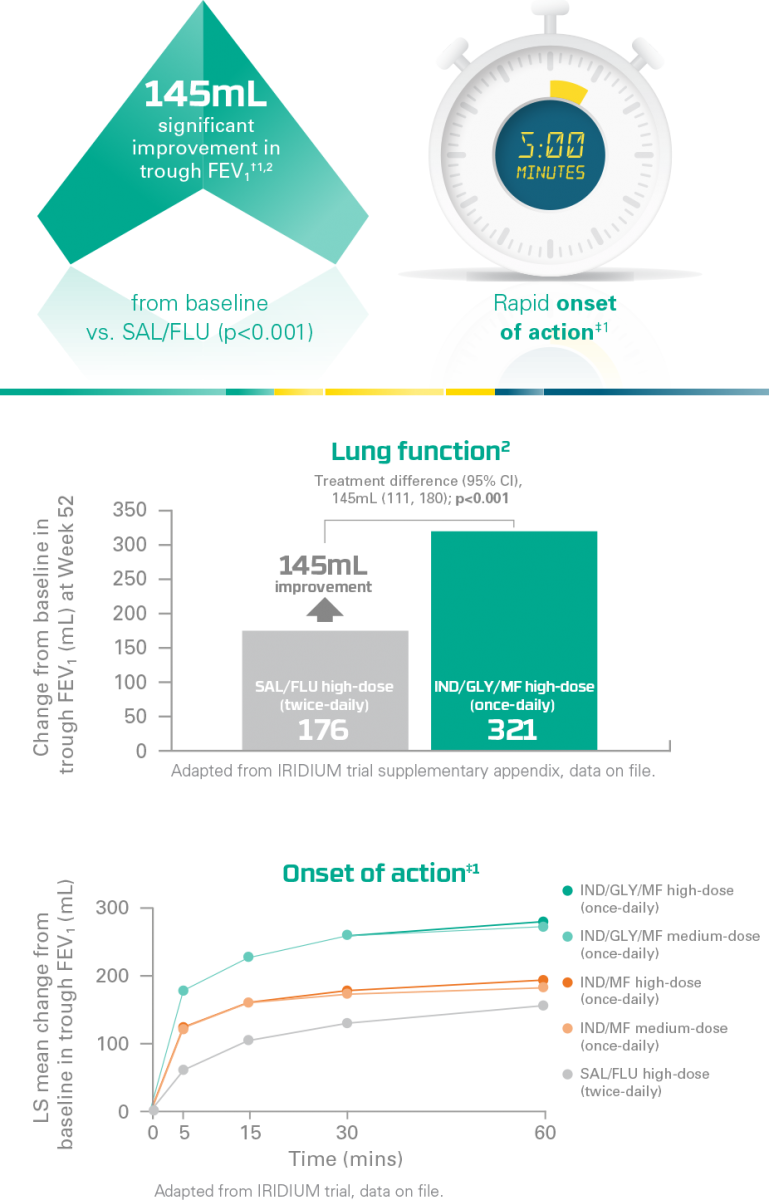
ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® improves patients’ ability to breathe*
In a secondary analysis,** ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® high-dose (once-daily) improved lung function vs. SAL/FLU high-dose (twice-daily)1
Primary endpoint:
Improvement in lung function with ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® high- and medium-doses vs. IND/MF high- and medium-doses was met1
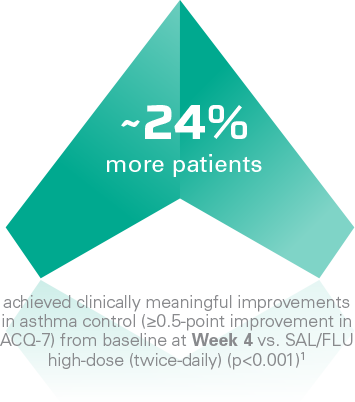
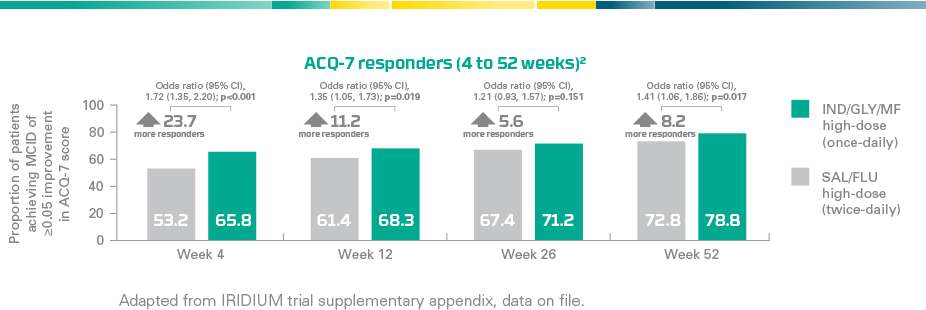
ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® improves asthma control*
A secondary analysis** demonstrated a higher proportion of ACQ-7 responders¶ with ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® high-dose (once-daily) vs. SAL/FLU high-dose (twice-daily)1
 |
Clinically meaningful improvement of asthma controlStatistically significant improvements in the proportion of ACQ-7 responders¶ at Weeks 4, 12 and 52 vs. SAL/FLU high-dose (twice-daily) (p≤0.019). Improvement was not statistically significant at Week 26 (p=0.151)1 Key secondary endpoint at Week 26 not met:No significant difference in the change in ACQ-7 score from baseline at Week 26 with ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® medium- and high-dose vs. corresponding doses of IND/MF (p=0.085 and p=0.729, respectively)1 |
IRIDIUM
 |
Improvements in asthma control (ACQ-7) already at Week 4 |
 |
Improved response to therapy at Week 52 vs. SAL/FLU high-dose (twice-daily) |
The ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® family has a favorable safety and tolerability profile1,3-5
Both ENERZAIR® BREEZHALER® and ATECTURA® BREEZHALER® were well-tolerated: AEs and SAEs were balanced & safety was comparable across treatment arms

To learn more about the Quartz, palladium, iridium and Argon studies, click here.
ACQ-7, asthma control questionnaire-7; AE, adverse events; CI, confidence interval; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; GLY, glycopyrronium; ICS, inhaled corticosteroid; IND, indacaterol acetate; LABA, long-acting beta2-agonist; MF, mometasone furoate; RR, rate ratio; SAE, serious adverse events; SAL/FLU, salmeterol/fluticasone propionate.
*In symptomatic asthma patients, despite treatment with medium- or high-dose LABA/ICS.1
**Secondary analysis, not controlled for multiplicity – analyzed using a generalized linear model assuming the negative binomial distribution.1
†Trough FEV1, defined as the highest bronchodilator effect on FEV1 approximately 24 hours after the last dose of each treatment period.1
‡As measured by FEV1 five minutes post-dose on Day 1.1
¶ ACQ-7 responder = patient achieving a minimal clinically important different of ≥0.5-point improvement from baseline in ACQ-7 score.1
REFERENCES:
-
Kerstjens H et al. Once-daily, single-inhaler indacaterol/glycopyrronium/mometasone versus indacaterol/mometasone or twice-daily salmeterol/fluticasone in patients with inadequately controlled asthma (IRIDIUM): a randomised, double-blind, controlled Phase III study. Lancet Resp Med; https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30190-9.
-
IRIDIUM trial supplementary appendix, data on file.
-
Van Zyl-Smit R. et al. Once-daily mometasone/indacaterol versus mometasone or twice-daily fluticasone/salmeterol in patients with inadequately controlled asthma (PALLADIUM): a randomised, double-blind, triple-dummy, controlled Phase III study. Lancet Resp Med; https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30178-8.
-
Kornmann O, et al. Respiratory Medicine. 2020;161:105809 [Epub ahead of print].
-
Gessner C et al. Fixed-dose combination of indacaterol/glycopyrronium/mometasone furoate once-daily versus salmeterol/fluticasone twice-daily plus tiotropium once-daily in patients with uncontrolled asthma: A randomised, Phase IIIb, non-inferiority study (ARGON). Resp Med 2020;106021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106021.
